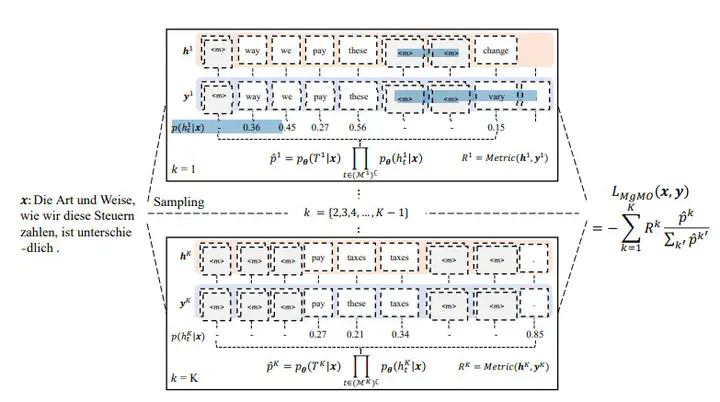
Abstract
Despite low latency, non-autoregressive machine translation (NAT) suffers severe performance deterioration due to the naive independence assumption. This assumption is further strengthened by cross-entropy loss, which encourages a strict match between the hypothesis and the reference token by token. To alleviate this issue, we propose multi-granularity optimization for NAT, which collects model behaviours on translation segments of various granularities and integrates feedback for backpropagation. Experiments on four WMT benchmarks show that the proposed method significantly outperforms the baseline models trained with cross-entropy loss, and achieves the best performance on WMT’16 En⇔Ro and highly competitive results on WMT’14 En⇔De for fully non-autoregressive translation.